Web Applications
- Web Application Planning
- PHP vs ASP.net Comparison
- Web Application Development Process
- Guide to Web Application Development
- Internet Database Development
- PHP & MySQL Development
CMS Applications
- What is Content Management System (CMS)
- Drupal vs Joomla vs WordPress CMS Comparison
- Enterprise CMS Comparison - Summary
- Enterprise Content Management System vs Open Source CMS - Detailed Guide, Security, Performance Statistics
- Pros and Cons of Wordpress, Joomla, Drupal
eCommerce Applications
- Enterprise eCommerce Platform Comparison
- Magento vs OScommerce vs Zen Cart Comparison
- Best eCommerce Software
- eCommerce SEO
Business Planning for Web Projects
- Internet / Online Business Ideas and Strategies for Entrepreneurs
- Web Development Cost Comparison
- Hiring a Web Application Company Considerations
- How to Hire a Good Web Application Development Company
- Challanges for hiring Offshore Web Development Company
- Guide to Merchant Account Payment Gateways
- e-Business Strategy and Process
Server Management and Hosting
- Dedicated / Managed Hosting Comparison
- Shared Hosting vs Managed Hosting
- Domains, DNS, Web Hosting, Email
- Domain Name System and DNS Servers
- All About Domain Name Registration
UNIX, LINUX & OS X File Permissions
To view permission information for all files and directories inside the current working directory, open a new terminal and type: ls -l
Here is an example of the output:
drwxr-xr-x 6 user group 204 Dec 30 06:37 images
-rw-r--r-- 1 user group 5754 May 20 2005 index.html
-rw-r--r-- 1 user group 9482 Jan 16 16:29 mypage.html
To view permission information for a particular file (for example:myfile.txt) type: ls -l myfile.txt
Here is an example of the output:
-rw-r--r-- 1 user group 9482 Jan 16 16:29 myfile.txt
Here is a quick reference and diagram of what "-rwxrw-r--" means:
"r" means: read permission
"w" means: write permission
"x" means: execute permission
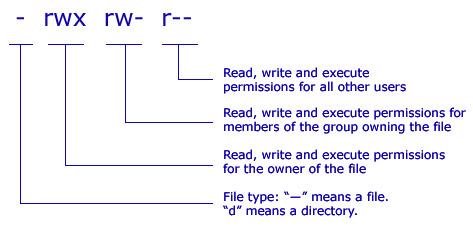
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| - | FIle type: " - " means a file. " d " means a directory |
| rwx | Read, write and execute permissions for members of the owner of the file |
| rw- | Read, write and execute permissions for members of the group owning the file |
| r-- | Read, write and execute permissions for all other users |
Changing file and folder permissions
Use the following commands to change file or folder permissions:
chmod (change file modes)
chown (change file owner)
chgrp (change file group owner)
The following letters represent
" u " - user/owner
" g " - group owner
" o " - all other users
" a " - for all: user/owner, group owner and all other users
" r " - read permission
" w " - write permission
" x " - execute permission
Examples of replacing and setting new permissions
(Note: Do not use space between any of the statements.
Example DO NOT TYPE: u = rwx)
# chmod u=rwx filename
# chmod u=rwx directoryname
# chmod -R u=rwx directoryname
# chmod g=rx filename
# chmod g=rx directoryname
# chmod -R g=rx directoryname
# chmod o=r filename
# chmod o=r directoryname
# chmod -R o=r directoryname
# chmod u=rwx,g=rx,o=r filename
# chmod u=rwx,g=rx,o=r directoryname
# chmod -R u=rwx,g=rx,o=r directoryname
# "-R" - means recursively change permissions of directories and their contents.
# chmod a=rwx filename
# "a" - for all: user/owner, group owner and all other users.
Examples of adding or taking away permissions from the current permissions
# chmod u+w filename
# chmod u+w directoryname
# chmod -R u+w directoryname
# chmod g+w filename
# chmod g+w directoryname
# chmod -R g+w directoryname
# chmod o-r filename
# chmod o-r directoryname
# chmod -R o-r directoryname
Modifying multiple permissions examples:
* chmod u+w,g+x,o-r filename
* chmod ug+rwx filename
* chmod ugo+rwx filename
* chmod u+w,g+x,o-r directoryname
* chmod ug+rwx directoryname
* chmod ugo+rwx directoryname
* chmod -R u+w,g+x,o-r directoryname
* chmod -R ug+w,o-r directoryname
* chmod -R ugo+rwx directoryname
* "-R" - means recursively change permissions of directories and their contents.
Examples of changing user/owner:
* chown username filename
* chown -R username directoryname
Examples of changing user/owner:
* chown username filename
* chown -R username directoryname
Examples of changing user/owner:
* chgrp groupname filename
* chgrp -R groupname directoryname
"-R" - means recursively change permissions of directories and their contents.
Here is some more examples:
chmod u=rwx,g=rw,o=rx myfile.txt
Now view the result:
ls -l myfile.txt
-rwxrw-r-x 1 user group 9482 Jan 16 16:29 myfile.txt
chmod -R u=rwx,g=rx,o=r directoryname
Now view the result:
ls -l directoryname
drwxr-xr-- 6 user group 204 Dec 30 06:37 images
-rwxr-xr-- 1 user group 5754 May 20 2005 index.html
-rwxr-xr-- 1 user group 9482 Jan 16 16:29 mypage.html
chown -R www directoryname
Now view the result:
ls -l directoryname
drwxr-xr-- 6 www group 204 Dec 30 06:37 images
-rwxr-xr-- 1 www group 5754 May 20 2005 index.html
-rwxr-xr-- 1 www group 9482 Jan 16 16:29 mypage.html
chgrp -R www directoryname
Now view the result:
ls -l directoryname
drwxr-xr-- 6 www www 204 Dec 30 06:37 images
-rwxr-xr-- 1 www www 5754 May 20 2005 index.html
-rwxr-xr-- 1 www www 9482 Jan 16 16:29 mypage.html
Comentum Corp
6222 Ferris Sq.
San Diego, CA 92121
Phone: 619-990-1212
Hours: Mon. - Fri., 9 a.m. - 5 p.m. PST
Contact Us »
Mobile App Development
iPhone, Google Android, BlackBerry, Windows Mobile
In-house development team.
San Diego, CA, USA.
Web App Estimator
Select and unselect modules such CMS or eCommerce for your web application and watch the cost update in real time.
Try It »
